Emergency Equine Vet:
Breadstone: 01453 811867
Failand: 01275 392956
Stretcholt: 01278 229129
Willesley: 01666 880501
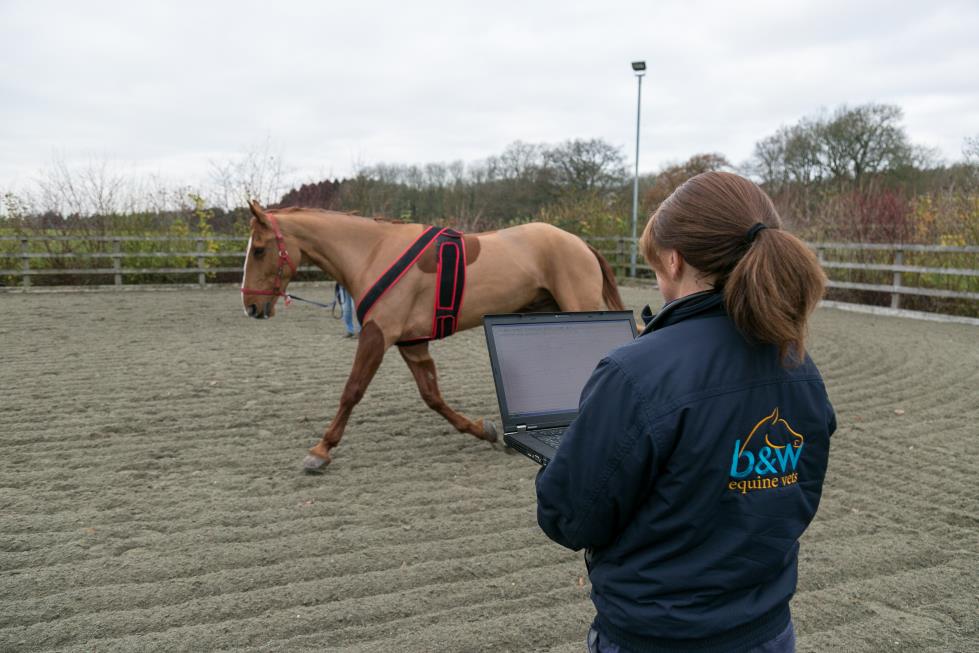
Horses may require cardiac evaluation when a cardiac abnormality is identified during a routine health examination or as part of investigation of poor performance or sickness. Cardiac evaluation most commonly involves electrocardiography (ECG) and echocardiography (heart scan). It may also require further tests such as blood tests (for example looking at electrolyte concentrations and markers of cardiac inflammation). ECG can be done at rest, during exercise or over a 24-hour period. These evaluations allow assessment of heart rate and rhythm, and identification of any arrhythmias as well as the frequency and situation when arrhythmias are occurring. Echocardiography is ultrasound imaging of the heart and is used to assess the structure and motion of the heart including flow of blood through the heart.
When an abnormal heart sound (murmur) or abnormal rhythm (arrhythmia) is identified at pre-purchase examination, cardiac examination can be performed to determine the likely significance of this abnormality. This will involve resting and exercising ECG (during the horse’s normal exercise) as well as echocardiography. The clinician will use this information to establish whether the abnormality is currently impacting the horse’s ability to perform at the expected level or if it is likely to impact this in the future.

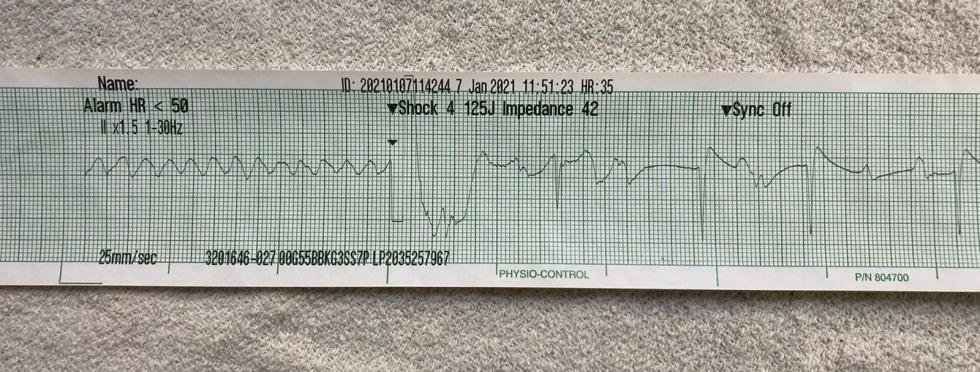
This arrhythmia is the most commonly treated condition of the equine heart. Investigation with ECG analysis and echocardiography will assess whether treatment is required. Treatment is performed either by administration of drugs (quinidine sulphate) or by electrical stimulation (transvenous electrocardioversion, TVEC). The relative merits of these two procedures vary depending on examination findings of the horse and how long atrial fibrillation has been present. Both procedures can be performed here at B&W Equine Hospital and equine medicine specialist Sarah Smith would be happy to discuss the treatment options with you.